
Mechanism of Action of NINLARO® (ixazomib)
NINLARO is a targeted, reversible proteasome inhibitor that is approved in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone for the treatment of relapsed multiple myeloma.1
Mechanism of Action (MOA)
Discover how proteasome inhibition with NINLARO works
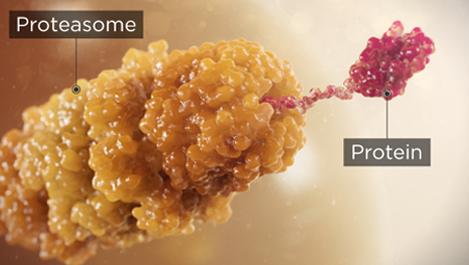
Proteasome inhibitors are a cornerstone of multiple myeloma treatment because cancer cells have a higher level of proteasome activity and are more sensitive to its proapoptotic effects3

NINLARO binds the β5 subunit of the 20S proteasome and inhibits its chymotrypsin-like activity1
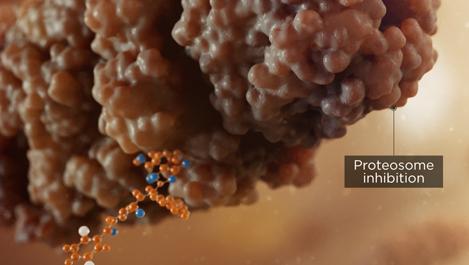
A buildup of proteins results from the inhibition of proteasome activity, leading to cytotoxicity and apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells2
Effects of proteasome inhibition with NINLARO
- NINLARO demonstrated in vitro cytotoxicity against myeloma cells from patients who had relapsed after multiple prior therapies1
- The combination of NINLARO + lenalidomide demonstrated synergistic cytotoxic effects in multiple myeloma cell lines1
NINLARO Mechanism of Action
Learn how NINLARO inhibits the action of proteasomes to induce apoptosis of myeloma cells.
ViewHide Transcript
Scene 1
Frame 1
Narration
The camera opens on the Takeda logo.
For two decades, Takeda has been a trusted partner and leader in the fight against multiple myeloma with a relentless focus on innovation,…
Frame 2
Narration
The logo begins to fade and the camera now shows a shot of a thigh bone.
…including pioneering proteasome inhibition with the first ever proteasome inhibitor, or PI…
Scene 2
Frame 1
Narration
The camera zooms into the bone marrow.
…in 2003 and subsequently bringing an oral proteasome inhibitor to patients in 2015 [1] [2].
Frame 2
Narration
We see plasma cells dividing uncontrollably.
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of the bone marrow, characterized by the irregular expansion of plasma cells [3][4].
Frame 3
Narration
We crash zoom further into a plasma cell of the tumor to see the proteasome.
The ubiquitin proteosome pathway allows for the degradation of proteins. The 26S proteasome is composed of a 20S proteolytic core [5].
Frame 4
Narration
We see a glow to indicate the protein function.
Therapeutic targeting of the proteasome has been a cornerstone of multiple myeloma treatment…
Frame 5
Narration
Call outs appear on the screen in time with the VO with the words 'Myeloma cells rely on the proteasome to survive', 'Proteasome Inhibitors (PIs) stop cell growth and cause cell death', and 'These therapies target the proteasome to treat multiple myeloma'.
… because the disruption of proteasome activity arrests cell growth and causes cell death [5].
Frame 6
Narration
This 20S core is made up of individual subunits which mediate proteolytic cleavage [5].
Frame 7
Narration
The 19S subunit is highlighted to draw attention.
When proteins are marked for degradation, they are recognized by the 19S cap and directed to the core of the proteasome [5].
Frame 8
Narration
The Beta subunits of the proteasome are now highlighted.
Proteolytic cleavage is mediated through Beta subunits [5].
Scene 3
Frame 1
Narration
The compound comes into frame, and we see a hero shot (NINLARO 4mg) as well as the NINLARO logo.
NINLARO or ixazomib is the only oral proteasome inhibitor and is indicated in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least one prior therapy. NINLARO is not recommended for use in the maintenance setting or in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone outside of controlled clinical trials [1].
Frame 2
Narration
The compound binds to the proteasome inhibitor through the Beta 5 subunit.
In vitro, NINLARO is a reversible proteasome inhibitor that preferentially binds to the Beta 5 subunit of 20S [1].
Frame 3
Narration
The proteasome is no longer functioning due to the presence of the compound.
It inhibits the chymotrypsin-like activity of the Beta 5 subunit [1] …
Frame 4
Narration
The environment turns slightly darker, and we see a build-up of proteins within the cell.
…disrupting the elimination of proteins which leads to cytotoxicity…
Frame 5
Narration
We zoom out slightly to view the mass of tumour cells. Cells in the tumour begin to disintegrate as cancer cell death is shown.
…inducing the apoptotic cascade and killing myeloma cells [6] .
Frame 6
Narration
We crash zoom back out of the bone marrow environment.
N/A
Scene 4
Frame 1
Narration
As part of an all-oral regimen, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, NINLARO may be a convenient option for patients at first relapse with multiple myeloma. NINLARO is not recommended for use in the maintenance setting or in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone outside of controlled clinical trials. [1][7].
Frame 2
Narration
We see a mosaic of patients enjoying their life outside example: diverse people gardening, elderly couple on a cruise, playing with grandchildren.
The NINLARO regimen may help facilitate long-term treatment until disease progression due to the convenience of oral administration and manageable safety profile [1].
Frame 3
Narration
On screen text with a graphic to indicate patients.
Text appears on screen: 'Those that have had at least one prior treatment when multiple myeloma comes back for the first time'
The NINLARO regimen may be prescribed to patients at first relapse who are experiencing an indolent relapse or elderly with an active lifestyle [1][3].
Scene 5
Frame 1
Narration
On-screen scrolling text in line with the VO, moving into ISI information.
NINLARO is also associated with these serious adverse reactions and drug interactions:
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Thrombocytopenia has been reported with NINLARO. Platelet nadirs typically occurred between Days 14-21 of each 28-day cycle and recovered to baseline by the start of the next cycle. Grade 3 thrombocytopenia was reported in 17% of patients in the NINLARO regimen and Grade 4 thrombocytopenia was reported in 13% in the NINLARO regimen. During treatment, monitor platelet counts at least monthly, and consider more frequent monitoring during the first three cycles. Manage thrombocytopenia with dose modifications and platelet transfusions as per standard medical guidelines.
Gastrointestinal Toxicities, including diarrhea, constipation, nausea and vomiting were reported with NINLARO and may occasionally require the use of antidiarrheal and antiemetic medications, and supportive care. Diarrhea resulted in the discontinuation of one or more of the three drugs in 3% of patients in the NINLARO regimen and 2% of patients in the placebo regimen. Adjust dosing for Grade 3 or 4 symptoms.
Peripheral Neuropathy was reported with NINLARO. The most commonly reported reaction was peripheral sensory neuropathy (24% and 17% in the NINLARO and placebo regimens, respectively). Peripheral motor neuropathy was not commonly reported in either regimen (<1%). Peripheral neuropathy resulted in discontinuation of one or more of the three drugs in 4% of patients in the NINLARO regimen and <1% of patients in the placebo regimen. During treatment, monitor patients for symptoms of neuropathy and consider adjusting dosing for new or worsening peripheral neuropathy.
Peripheral Edema was reported with NINLARO. Evaluate for underlying causes and provide supportive care, as necessary. Adjust dosing of NINLARO for Grade 3 or 4 symptoms or dexamethasone per its prescribing information.
Cutaneous Reactions. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, including fatal cases, have been reported with NINLARO. If Stevens-Johnson syndrome occurs, discontinue NINLARO and manage as clinically indicated. Rash, most commonly maculo-papular and macular rash, was reported with NINLARO. Rash resulted in discontinuation of one or more of the three drugs in <1% of patients in both regimens. Manage rash with supportive care or with dose modification if Grade 2 or higher.
Thrombotic Microangiopathy has been reported with NINLARO. Fatal cases of thrombotic microangiopathy, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome (TTP/HUS), have been reported in patients who received NINLARO. Monitor for signs and symptoms of TTP/HUS. If the diagnosis is suspected, stop NINLARO and evaluate. If the diagnosis of TTP/HUS is excluded, consider restarting NINLARO. The safety of reinitiating NINLARO therapy in patients previously experiencing TTP/HUS is not known.
Hepatotoxicity has been reported with NINLARO. Drug-induced liver injury, hepatocellular injury, hepatic steatosis, hepatitis cholestatic and hepatotoxicity have each been reported in <1% of patients treated with NINLARO. Hepatotoxicity has been reported (10% in the NINLARO regimen and 9% in the placebo regimen). Monitor hepatic enzymes regularly and adjust dosing for Grade 3 or 4 symptoms.
Embryo-fetal Toxicity: NINLARO can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with NINLARO and for 90 days following the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with NINLARO and for 90 days following the last dose.
Increased Mortality in Patients Treated with NINLARO in the Maintenance Setting: In two prospective randomized clinical trials in multiple myeloma in the maintenance setting, treatment with NINLARO resulted in increased deaths. Treatment of patients with NINLARO for multiple myeloma in the maintenance setting is not recommended outside of controlled trials.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in the NINLARO regimen compared to placebo in combination with lenalidomide plus dexamethasone, respectively were thrombocytopenia (85%, 67%; pooled from adverse event and laboratory data), neutropenia (74%, 70%; pooled from adverse event and laboratory data), diarrhea (52%, 43%), constipation (35%, 28%), peripheral neuropathy (32%, 24%), nausea (32%, 23%), edema peripheral (27%, 21%), rash (27%, 16%), vomiting (26%, 13%), and bronchitis (22%, 17%). Serious adverse reactions reported in ≥ 2% of patients in the NINLARO regimen included diarrhea (3%), thrombocytopenia (2%), and bronchitis (2%).
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Avoid concomitant administration of NINLARO with strong CYP3A inducers.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with NINLARO and for 90 days after the last dose.
- Hepatic Impairment: Reduce the NINLARO starting dose to 3 mg in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment.
- Renal Impairment: Reduce the NINLARO starting dose to 3 mg in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis. NINLARO is not dialyzable.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda Pharmaceuticals at 1-844-217-6468 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please see NINLARO (ixazomib) full Prescribing Information.
Scene 6
Frame 1
Narration
The graphics disappear and we are back on the previous footage of the patient mosaic.
The NINLARO regimen may provide the benefits of long-term proteasome inhibition, defined as treatment until disease progression [1].
Frame 2
Narration
Continuation of previous frame, closing on NINLARO and Takeda logos.
The NINLARO regimen may offer extended efficacy and manageable tolerability for the types of patients with relapsed multiple myeloma you see everyday [1][8][9][10][11].
REFERENCES:
- NINLARO. Prescribing Information. Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.; 03/2024: https://www.ninlaro.com/prescribing-information.pdf. Accessed June 2024.
- VELCADE. Prescribing Information. Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.; 08/2022: https://www.velcade.com/files/pdfs/VELCADE_PRESCRIBING_INFORMATION.pdf. Accessed June 2024.
- Raedler LA. Ninlaro (Ixazomib): First Oral Proteasome Inhibitor Approved for the Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2016;9(Spec Feature):102-105.
- Mahindra A, Hideshima T, Anderson KC. Multiple myeloma: biology of the disease. Blood Rev. 2010;24 Suppl 1:S5-S11.
- Moreau P, Richardson PG, Cavo M, Orlowski RZ, San Miguel JF, Palumbo A, Harousseau JL. Proteasome inhibitors in multiple myeloma: 10 years later. Blood. 2012;120(5):947-959.
- Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Richardson P, Anderson KC. Proteasome inhibitor therapy in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4(4):686-692.
- Muz B, Ghazarian RN, Ou M, Luderer MJ, Kusdono HD, Azab AK. Spotlight on ixazomib: potential in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:217-226.
- Moreau P, Masszi T, Grzasko N, et al; for TOURMALINE-MM1 Study Group. Oral ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(17):1621-1634.
- Terpos E, Ramasamy K, Maouche N, et al. Real-world effectiveness and safety of ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol. 2020;99(5):1049-1061.
- Minarik J, Pika T, Radocha J, et al. Survival benefit of ixazomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (IRD) over lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma patients in routine clinical practice. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):73.
- Hájek R, Minařík J, Straub J, et al. Ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone in routine clinical practice: effectiveness in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Future Oncol. 2021;17(19):2499-2512.
PHARMACOKINETICS (PK)
Absorption and distribution
- After NINLARO oral administration, the median time to achieve peak plasma concentrations was 1 hour1
- The mean absolute oral bioavailability was 58%, based on population PK analysis1
Metabolism and elimination
- The terminal half-life of NINLARO is 9.5 days1
- There was no clinically meaningful effect of age, sex, body surface area, or race on the clearance of NINLARO based on population PK analysis1
NINLARO patient profiles
Different patient types with relapsed multiple myeloma may benefit from the NINLARO triplet regimen.
NINLARO dosing
Find the dosing schedule for the NINLARO all-oral triplet regimen and information on dosage modifications.